Dive In
The Industrial Revolution: Great leaps, greater opportunities

The Industrial Revolution is one of the most significant events in world history. It refers to a period of massive economic, technological, social, and cultural changes. It began in the United Kingdom in the 1700s and spread to the rest of the world. A mainly agriculture-based world economy using manual labour was transformed into an industrial and manufacturing global economy through the introduction of machines. This revolution passed through four stages that shaped the industrial communities.
The First Industrial Revolution took place from the end of the 18th century to the beginning of the 19th century. This period was characterised by developments in textiles, iron and steam. It witnessed the emergence of mechanisation that replaced manual labour and changed the economic structure of the society. After that, the mass extraction of coal came, along with the invention of the steam engine, which enhanced the development of railroads and accelerated economic, human, and material advancement.
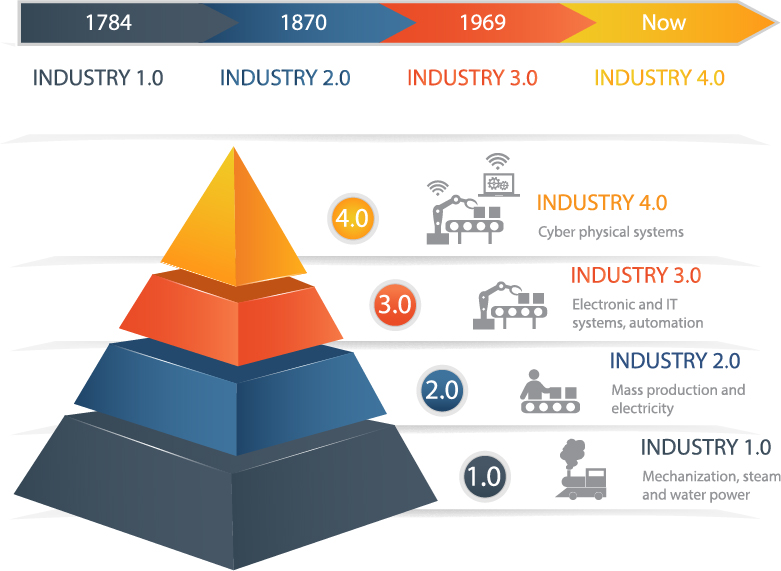
During the 19th century, as a result of Britain’s success, countries rushed to emulate the revolutionary economic model. Laws were passed to regulate rights and duties of workers, upon trade unions’ demands, which developed the social security legislation against accidents, unemployment, and illness.
Nearly a century later, the Second Industrial Revolution initiated new technological advancements with the emergence of electricity, gas, and oil. This period was characterised by the industry of steel. Methods of communication and transportation were revolutionised with the invention of the telegraph, telephone, automobiles, and planes.
By the end of the 20th century, a Third Industrial Revolution appeared with new energy which surpassed its predecessors: nuclear energy. It witnessed the rise of electronics, telecommunications, and computers, and led to the production of miniaturised material, which progressed to space research and biotechnology. This revolution increased the level of automation in industrial production with the inventions of automatons and robots.
In the 21st century, with the widespread of the Internet, Professor Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum, coinedtheterm Fourth Industrial Revolution, also known as “Industry 4.0.” This revolution rooted a new technological phenomenon of digitalisation. It built a new virtual world which lead the physical one and aimed to connect all production means, by using Big Data Analytics and the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT). The mechanisms and tools of this revolution reduced operating costs, improved the level of profits, and worked to raise the efficiency of human capital.
Today, the world is entering a new phase that requires a dynamic work environment and equipping future leaders with the skills to take advantage of modern technologies and open new economic sectors.
The South African model
South Africa is one of the most prosperous countries in industry, due to the rapid and promising technological transformation process, over the past few years. The existence of political and legislative responses to the digital revolution helped maximise the expected benefits and minimise the effects of negative consequences, especially with the government announcing the intention to provide training for automation, digital transformation, and Artificial Intelligence (AI), at all educational levels, to be used in the light of industrial development and job creation.
The Emirati model
Another unique model is the United Arab Emirates, which is keeping pace with the Fourth Industrial Revolution and employing technology to serve the community and promote social cohesion. The government of the UAE launched a number of initiatives and legislations to allow a suitable environment for different technologies, as part of a new concept to make the government a dynamic platform for innovation, rather than a purely legislative body, with ultimate support for human empowerment.
Egyptian reforms and opportunities
In Egypt, the industrial sector witnessed great leaps in the last 5 years, under the leadership of President Abdelfattah El-Sisi. The current government focuses on Egypt’s comparative advantages and the use of the latest methods of global technology.
Egypt took significant measures and reforms in its implementation of Egypt Vision 2030, and its economic and social reform programme. The programme is based on reforming the existing legislative and institutional system and issuing new laws, in addition to supporting the partnership between public and private sectors, creating the necessary infrastructure to attract investors, developing small and medium enterprises, encouraging the integration of the informal sector into the formal one, and fostering entrepreneurship and training to qualify human cadres.
Egypt aims to gradually raise the economic growth rate to 8% in 2021/22, up from 5.3% in 2017/2018, through continued efforts to improve the business environment. Egypt also targets boosting the competitiveness of the industrial sector to raise its growth rate from 6.3% in 2018/2019 to 10.7% in 2021/2022.
To sum up, the world is changing faster than ever; the Industrial Revolution represented a major turning point in history, affecting almost every aspect of daily life. Today, a Fourth Industrial Revolution is underway with exponential expansion by merging technologies, offering endless possibilities for a cooperative and interconnected industrial global system.
Today, Egypt is taking serious steps to reach a digital society and achieve financial inclusion, through comprehensive and sustainable development, and a general culture of hard work, taking risks, and developing ideas. Egypt is back on the industrial track, and if you want to seize the opportunity, it is high time to invest here.
Share



